Tuesday, February 03 2015
You might recently have heard on the news that a 14-year-old boy was airlifted out of Mission Trails Regional Park in San Diego, California after a rattlesnake bit his leg. In Arizona, an adult was badly bitten on the knuckle of his middle finger. At the hospital, the man who nearly lost his finger from the bite said, "It felt like having your finger injected with molten lava. The pain was intense and immediate, the swelling was dramatic, almost instantaneous." He had to be treated with 23 vials of costly anti-venom.
Isn't it too early in the season to have to worry about snake bite? Shouldn't these venomous creatures still be hibernating until March or April? Well, that depends. A warmer than expected winter in some places has caused snakes to come out of hibernation earlier than usual. In fact, in warmer southern states, snakes often don't go into hibernation at all. Instead, they go into "brumation."
Hibernation is a deep sleep, usually occuring in colder, snow covered climates in northern states. Snakes don't actually sleep in brumation, but their bodies acclimate to a lower temperature, their metabolism slows, and they become less active and less inclined to feed. Brumation or hibernation is necessary for breeding. If male snakes don't cool down at some point during the year, they most likely would not be able to produce fertile sperm.
On warm days, brumating snakes sometimes come out of their dens to bask in the sunshine. Nice sunny winter days are often when people are surprised by snakes. Just like humans, snakes head out to enjoy the sun and unsuspecting hikers can startle them and cause them to strike. As a rule of thumb, rattlesnakes can strike a distance of two-thirds their total body length. That means a three foot long snake may be able to strike a distance of two feet. The best advice is to stay alert when recreating in environments where snakes are known to live. If you see a snake or hear it rattle, take one big step back so you're immediately out of striking range. Rattlesnakes usually try to get way from people and bite only when attacked -- or when they perceive they are being threatened or attacked. Many bites occur when snakes are accidentally stepped on. Wear snake gaiters or snake proof boots and you'll know you're protected in case that happens.
Generally, rattlesnakes emerge from hibernation in March or April, or when the average daytime temperatures reach and remain about 60 degrees Fahrenheit and higher. In the spring, keep in mind that emerging snakes are hungry, thirsty, and ready for love! They are most active in 80-degree temperatures. With spring approaching, follow the Boy Scout motto and be prepared. Whether you are of the mindset that rattlers and other dangerous snakes have their place in the ecosystem and should be left alone when encountered, or think the only good rattler is a dead rattler, don't take a chance. Wear snake gaiters or snake boots and you'll know you're protected when in the desert or woods.
Friday, November 28 2014
When snakes in the wild go into hibernation depends on two things: their location and their species. A snake in Minnesota will go into hibernation much earlier than a snake in Texas, and come out of hibernation much later. Snakes from tropical climates, such as pythons and boas, don't hibernate at all. Venomous snakes from North America, such as rattlers, copperheads, and cottonmouths, hibernate when the weather cools down. Snake activity picks up as temperatures fall in late summer and early autumn before they go into hibernation, which can be as early as September or as late as December. Generally, rattlesnakes emerge from hibernation in March or April, or when the average daytime temperatures reach and remain about 60 degrees Fahrenhei t and higher. t and higher.
In warmer southern states, snakes often don't go into hibernation, but brumation. Hibernation is a deep sleep, usually occuring in colder, snow covered climates in northern states. Snakes don't actually sleep in Brumation, but their bodies acclimate to a lower temperature, their metabolism slows, and they become less active and less inclined to feed. Brumation or hibernation is necessary for breeding. If male snakes don't cool down at some point during the year, they most likely would not be able to produce fertile sperm.
On warm days, brumating snakes sometimes come out of their dens to bask in the sunshine. Nice sunny winter days that follow a long cold snap are often when people are surprised by snakes. Just like humans, snakes head out to enjoy the sun and unsuspecting hikers can startle them and cause them to strike. As a rule of thumb, rattlesnakes can strike a distance of two-thirds their total body length. That means a three foot long snake may be able to strike a distance of two feet. Rattlesnakes cannot jump. If striking downhill, however, gravity and the momentum generated by a strike may combine to carry the animal farther forward than would occur over flat ground. On very steep slopes, a snake could lose balance during a strike and actually fall toward its target. Thus, the effective range of a downhill strike may exceed that normally expected across a level surface.
Caves and deep crevices on rocky hillsides are common hibernaculums for rattlers. Many species hibernate in groups. Rodent burrows are probably the most common places for sleeping snakes, especially in southern states such as Texas. Other places include holes under the roots of a tree or inside a rotting log. Barns or under houses are other good spots for snakes. Not all snakes will survive hibernation. A skinny snake will not survive. If the snake feeds heavily before they hibernate, and have digested their meal before the cooling starts, they will be OK. If food is in their stomach or intestines when they cool, it will rot and kill them.
Snakes are most active whenever temperatures are between 80-90F. This means that the snakes may be active most of the day during the spring, and during the early mornings and late afternoons throughout the summer. Exposure to temperatures above 110F for more than a few minutes is enough to kill a rattlesnake; therefore, during the hottest part of summer, snakes are seldom observed, except occasionally at night. Snake activity picks up again as temperatures begin to fall in late summer and early autumn before they go into hibernation or brumation.
An estimated 45,000 people are bitten by snakes annually in the United States. Approximately 8,000 of these bites are from venomous snakes. It is estimated that snakebites account for 125,000 deaths worldwide each year. Those statistics are enough reason to always wear snake boots or snake gaiters when in snake country, which could be the desert or the woods. If you do, you won't have to worry so much about the temperature or the season because if you use common sense and wear snake bite protection, you'll keep yourself safe.
Saturday, August 02 2014
The unseasonably warm weather is bringing rattlesnakes out of hiding, resulting in larger numbers of people being bitten this spring and summer. And while snakes are found in both dry and wet environments, did you know that wood piles are one of the most common places for rattlers and other snakes to hide? Recently, a victim in San Bernardino County, California was tidying up a wood pile in his back yard. He reached for a log and felt a sudden burning sensation in his arm. Not two weeks l ater, also in southern California, another man building a firewood pile on his property was bitten by a juvenile rattlesnake, later identified as a Southern Pacific rattlesnake, also known as a Western rattlesnake. This particular type of rattlesnake is native to California and has highly toxic venom. The venom of the Southern Pacific rattlesnake is so toxic that it requires more antivenin than other types of rattlesnakes and packs a potentially lethal punch. Wearing protective gloves and snake gaiters on your lower legs is an easy and inexpensive safety precaution when working in snake habitat. ater, also in southern California, another man building a firewood pile on his property was bitten by a juvenile rattlesnake, later identified as a Southern Pacific rattlesnake, also known as a Western rattlesnake. This particular type of rattlesnake is native to California and has highly toxic venom. The venom of the Southern Pacific rattlesnake is so toxic that it requires more antivenin than other types of rattlesnakes and packs a potentially lethal punch. Wearing protective gloves and snake gaiters on your lower legs is an easy and inexpensive safety precaution when working in snake habitat.
Why wood piles? Snakes cozy up in many places— rock walls, ledges, under bushes— but many times snakes live where their food supply is plentiful. Mice and rats like to build their nests in wood piles. Get rid of rodents and you will remove a major source of rattlesnake attractant. This is especially important around areas where animal food is stored on farms. The height of activity for snakes is during summer, and especially at night. If you have woodpiles, you want them 12 to 16 inches above the ground. It doesn't give a place for the snakes to hide.
If a rattlesnake feels threatened it will often times release its venom. The venom can clog your blood and shut down your respiratory system. Rattlesnake venom works like acid in the body, killing the living cells it touches. If you get bitten, it is going to hurt, it is going to swell, and you are going to have tissue damage. If not treated quickly, a bite in the arm or leg could cause irreversible damage to that limb. It is important to keep the wound immobilized below the heart so that the venom spreads less quickly. It is critical to receive immediate medical attention.
Besides the damage and pain that can be caused by a bite, you will likely face high medical expenses. A victim of a rattlesnake bite is given between 10 and 15 anti-venom vials. Each of those vials costs between $2,000 and $5,000! Wearing protective snake gaiters or snake boots is an easy and inexpensive safety precaution for not only working around woodpiles, but when hiking or camping in the desert or woods. Be safe and not sorry— wear snake bite protection!
Sunday, June 22 2014
The official start of summer means more people are generally spending more time outdoors, which also means their dogs are with them, especially when hiking and camping. Rising temperatures can also mean more snakes are active, resulting in the risk of more snake bites for both humans and animals. Of course if you spend a lot of time in "snake country" (could be the de sert or woods, depending on where you live) you either wear snake proof boots or snake gaiters over your own thick leather boots, but what about Fido? Unfortunately there are no such products for canines, but even if there was, you might have a hard time convincing your pooch to wear them. So what can you do to keep your dog safe from snake bite? Check out rattlesnake avoidance training! sert or woods, depending on where you live) you either wear snake proof boots or snake gaiters over your own thick leather boots, but what about Fido? Unfortunately there are no such products for canines, but even if there was, you might have a hard time convincing your pooch to wear them. So what can you do to keep your dog safe from snake bite? Check out rattlesnake avoidance training!
"Prevention is your number one line of defense in protecting your dogs from venomous snakes. When dogs and their owners go hiking, camping, or to the park where dogs go off leash, this training teaches them to be fearful of the rattlesnake. It also protects the people as well, as the dog becomes an alert system. This training has proven to be an effective tool in teaching rattlesnake avoidance to all dogs from Great Danes to Chihuahuas," explains John Potash, co-founder and co-owner of Get Rattled.
Get Rattled is a unique training clinic designed specifically to teach dogs on rattlesnake avoidance. The clinic has been in business for 14 years and has successfully trained more than 5,000 dogs. Potash is licensed by the Nevada Department of Wildlife and has 24 years of experience working with venomous snakes and wildlife in areas of animal control, wildlife rescue, and public education. He works with skilled dog trainer Willie J. Stevens Jr. who has more than 20 years of experience training and judging pointing dogs. The training is held at Olive Hills Kennels in Knights Landing, California. If you live in a different state that is known to have a problem with snakes, ask around or search cyberspace for a similar training program near you.
But what happens if your beloved canine gets bitten despite your best efforts to protect him or her? Dogs are usually bitten on their front limbs, neck, head, or face so look for bleeding and severe swelling in those areas. A dog will often act as though something is bothering them by rubbing or licking the affected area. After some time, the venom may produce nausea, vomiting, and the dog can seem lethargic. If you see a snake bite happen or notice these symptoms, keep your dog calm and get to a vet right away.
 If your vet determines that your dog has been bitten by a rattlesnake, he or she can administer an anti-venom shot. Veterinarians in areas that are experiencing higher than usual incidences of snake bit in dogs also recommend a vaccine booster shot every six months. The vaccine is important not only because it can help limit the damage done by snakebite, but also because it costs far less than the anti-vemon. Although the vaccines cannot prevent a dog from suffering a snakebite, and they aren’t effective against all snakes found in all states, vets have reporting seeing plenty of dogs who are alive because they received the vaccine booster. The vaccine is effective against bites from western rattlesnakes and timber rattlesnakes, but not eastern rattlesnakes or water moccasins. If your vet determines that your dog has been bitten by a rattlesnake, he or she can administer an anti-venom shot. Veterinarians in areas that are experiencing higher than usual incidences of snake bit in dogs also recommend a vaccine booster shot every six months. The vaccine is important not only because it can help limit the damage done by snakebite, but also because it costs far less than the anti-vemon. Although the vaccines cannot prevent a dog from suffering a snakebite, and they aren’t effective against all snakes found in all states, vets have reporting seeing plenty of dogs who are alive because they received the vaccine booster. The vaccine is effective against bites from western rattlesnakes and timber rattlesnakes, but not eastern rattlesnakes or water moccasins.
Not all dog owners need to worry about vaccinating their pet, especially if your furry family member is primarily an indoor animal. But if Rover lives outside, like a hunting dog, or if your pet tends to wander around or is your hiking companion, talk to your local veterinarian about getting the vaccine.
Sunday, May 18 2014
It's rattlesnake season again! Most people fear those words, but a few actually relish this time of year. Are they crazy? Well, not exactly. Some folks have a job that involves tracking and catching snakes for research or preservation.
Take, for example, Ann Stengel in Sheffield, Massachusetts. Ms Stengel is a UMass Amherst doctoral candidate out to save the timber rattlesnake in New England. It turns out that the rattlesnake populations are endangered in that region. The largest population left in Massachusetts—and possibly in New England—is found in Berkshire County. Human incursion into habitat and malicious killing of the snakes have greatly disturbed their numbers. And given that female snakes only reproduce once every three to five years and 80 percent of offspring can be expected to die in the first year, the snakes are slow to rebuild depleted populations.
In the name of science, people like Stengel take newborn snakes into captivity for a year or a year and a half, then release them near their den site with the hope that they adapt back into the wild. Some do and some don't. The more successful this project becomes, the more people who find rattlers fearsome will object to it. In response, Ms. Stengle points out that snakes are good for rodent control, and that to date no one in Massachusetts has ever died of a rattlesnake bite. In fact, bites are extremely rare as timber rattlesnakes, the species found in the Berkshires, are not very aggressive.
A bride-to-be in El Dorado County, California wishes the rattlers in her area were not aggressive. Instead of marching down the aisle to say "I Do" Macee Whitton found herself in the hospital on her wedding day. A week before her Big Day, she was outside with her dogs and a rattlesnake bit her on the ankle. Despite getting bags of anti-venom at a nearby medical center, the poison kept traveling through her body. She had a lengthy hospital stay and it took weeks to recover. Her wedding has been rescheduled.
According to the California Poison Control Center, most bites occur between April and October when snakes and humans are most active outdoors. The vipers usually den from late October to early April. Their body temperature will get down to 40 degrees. They lose very little body weight because they shut down metabolically. A female rattler is pregnant for more than a year before giving birth to eight to 12 live little snakes. You might think the mother rattler then slithers off and leaves the little ones to fend for themselves, but researcher shows that the mother remains with her young until she leads them to the family den at the end of fall. There, the little ones, their mother and 30 to 50 other snakes will disappear deep into the ground below the frost level to sleep away the winter.
Once the snakes emerge from hibernation at this time of year, they have a kind of social life. They often use the same basking areas, and are particularly fond of south-facing rocky slopes. During the warm months snakes will travel— males up to four miles and non-pregnant females about two miles. But they always return to the same den. An adult rattler can live for 45 years if it avoids predators such as humans and red-tailed hawks.
The best thing you can do when in rattlesnake country is not to avoid the great outdoors, but to be prepared by wearing snake gaiters or snake proof boots. And don't ever let your guard down. Keep an eye out, be careful of where you sit, and don't reach into blind areas under rocks or wood piles where rattlesnake hang out.
Friday, March 28 2014
You might be wondering why on earth anyone would want to purposely ROUND UP a bunch of rattlesnakes. After all, most people do their best to avoid them. But if you're a rancher or farmer in Sweetwater, Texas who lose cattle to these vipers, you look forward to getting rid of as many as possible. Since 1958, the World's Largest Rattlesnake Round-Up has been held annually on the 2nd weekend in March at the Nolan County Coliseum. The Round-Up was started as a way to control the population of snakes in this area of Texas, and has turned into a popular annual event sponsored by the Sweetwater Jaycees.
Today, the Rattlesnake Round-Up draws over 40,000 visitors per year and is fun for the whole family. You can expect a Snake Safety Demonstration , Fried Snake Meat, Vendors of all kinds, a Carnival, Flea Market, a Miss Snakecharmer Pageant, a Gun Knife & Coin Show— lots of things to see and do. But even with all the other things going on, the rattlesnakes are the main attraction. Bus tours take people out on tours so you get a feel for the rattlesnake's habitat.  It's really educational! It's really educational!
The Jaycees purchase about 5,000 pounds of rattlesnakes each year from private hunters who trap them. Not to worry, as you'll see in the video, everyone coming into contact with these fearsome creatures uses snake bite protection such as snake chaps and long-handled snake hooks.
After being "rounded up" the venom is removed from each viper. Then they are weighed, measured, and sexed. The data is used by the wildlife department. The rattlesnakes then literally lose their head, but nothing is wasted. The hides are used for wallets and belts and other decorative items. The meat becomes part of the BBQ menu that Texas is known for.
If you've never been to Sweetwater, the city is located in Nolan County, 40 miles west of Abilene, 75 miles north of San Angelo, 125 miles southeast of Lubbock, 130 miles of Odessa and 190 miles west of Ft. Worth. The landscape is predominantly rolling uplands to the north, with plateaus traversed by valleys in the south. The agricultural economy centers around cattle and live-stock products, but 50 percent of the annual agricultural income is from crops, especially cotton, wheat and sorghum that favor loamy soil. Wind power is fast becoming an alternative energy source of choice— Nolan County is one of the Top 10 largest wind farms in the United States.
If you like history, you'll enjoy the stories that put Nolan County on the map. The first Anglo settlers, mostly buffalo hunters, came to the area after the Civil War. Knight's store on Sweetwater Creek was started in a dugout in 1877 to serve the buffalo hunters . The county's first post office was opened in 1879 in the village of Sweet Water, which was two words until the spelling was officially changed in 1918. The original name of the post office was Blue Goose, derived from a story that the first postmaster ate a blue crane that cowboys told him was a blue goose. The townsite was on the Texas and Pacific Railway, which had built into the area in March 1881. The first newspaper was published that same year.
If the World's Largest Rattlesnake Round-Up sounds oddly interesting and you would like to learn more about the snakes and safely see them close up, mark your calendars and visit Sweetwater, Texas next year. The event is always held the second weekend of March.
Saturday, February 22 2014
We all know that there's a specific purpose to a snake's rattle— to scare larger animals and humans away. And it generally works! Hearing that rattle signals immediate danger and most of us move away as quickly as possible. But what if you couldn't hear the rattle and be warned? What if you sat down on a log or were walking down a trail and didn't know that a snake was inches from you because there was no warning rattle?! Some experts say that's what is happening with the Crotalus Viridis¸ or the prairie rattlesnake in the Black Hills of South Dakota. 
Over the past couple of years, naturalists have noticed many rattlesnakes with “curly-Q” tails, like you find on pigs. The tail muscles on these snakes have atrophied and can’t move the rattle. Snakes that have this genetic defect are the ones that are surviving. They reproduce and pass along that genetic defect to their offspring. The benefit to the snake is that if they are not heard, they are not killed. Because when most people hear that chilling rattle, if they have a garden shovel or gun available, it's all over for the snake.
Most people WANT to hear the rattle. It's helpful to both snakes and humans. These reptiles don't really want to bite humans— that would be a waste of venom on something they can't eat. So rattling warns us to get away, saving both species. Two hundred years ago when Native Americans were the only people in South Dakota, a rattlesnake would rattle and they would respect it and leave it alone. When white settlers moved in, however, and heard a rattlesnake rattle, they instantly killed it. So perhaps this genetic abnormality is actually saving rattlesnakes from certain death by humans?
There is no scientific data to back up this theory other than from observing that the rattlesnakes are developing this behavior, but it's worth keeping in mind for those who spend a lot of time in the desert or woods where rattlesnakes live. Keep in mind that if someone is bitten by a rattlesnake, the old wives tales about sucking out the poison, drinking alcohol, and other methods work won’t. The best thing is to carry basic First Aid supplies in your backpack, and then get help right away— get to a hospital and get anti-venom. Better yet, don't take a chance. Wear light-weight snake gaiters or snake boots and you won't have to worry about getting bitten— whether that snake is able to send a warning rattle or not.
Wednesday, January 01 2014
Did you know that rattlesnakes regulate the volume of their venom? A mouse needs only a little dose and a rat a little more. A rabbit may receive a little more venom than a rat. Rattlers sometimes bite humans without injecting venom. A snake that feels in danger may "deliver everything it has." About 6,000 people are bitten in North America each year. In about 80 percent of those cases, experts say, the victim was trying to handle the snake. A half century ago, fatalities were common. Not so today. Medical treatment is usually nearby, and antivenin is effective. Only one in about 700 bites results in death. If you don't die, the greatest danger is hock caused by dangerously low blood pressure that can deprive the brain and other organs of oxygen. Some snakebite victims bleed internally. Even with treatment, a survivor might lose flesh, muscle tissue, nerves, bone, even a limb.
Don't think rattlesnake venom is all that bad? Think again. A well-known snake expert, 61-year old Joe Wasilewski, was recently bitten in Florida and nearly lost his life. And that was someone who knew what he was doing— someone who has handled hundreds thousands of snakes during the last 50 years. Someone also used to handling crocodiles. But all it took was one mean viper to "deliver everything it has" and this expert almost didn't make it. Writer Jeff Klinkenberg of the Tampa Bay Times reported the story:
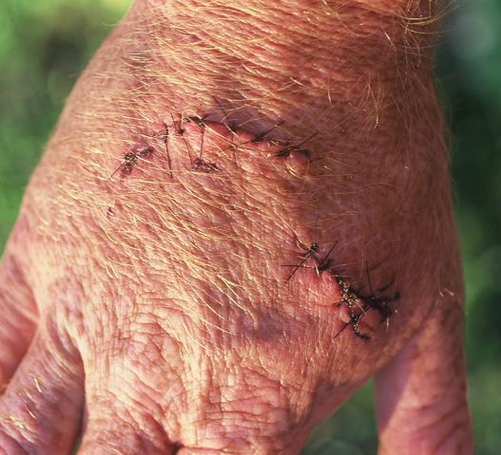 Wasilewski had opened a cage and used a short pole to lift a buzzing 4-foot diamondback rattlesnake. In a well-practiced move, he slid the snake into a garbage can for safekeeping while he cleaned the cage. Then it was time to reverse the process. Hook the snake in the middle, position head away from you, slide it back into the cage. But then Joe felt a sharp sting in his left forearm. Wasilewski had opened a cage and used a short pole to lift a buzzing 4-foot diamondback rattlesnake. In a well-practiced move, he slid the snake into a garbage can for safekeeping while he cleaned the cage. Then it was time to reverse the process. Hook the snake in the middle, position head away from you, slide it back into the cage. But then Joe felt a sharp sting in his left forearm.
"Oh, oh,'' he told his son, Nick. "I think he got me.'' While his son called 911, Wasilewski got a funny metallic taste in his mouth. His lips tingled, he sweated profusely, he threw up. By the time he was taken to the hospital, Wasilewski was unconscious. His blood wasn't clotting. He'd received eight vials of antivenin. Then he got another eight. His arm was grotesque and swollen. Standing next to his dad's bed in intensive care, Nick stared in shock at the stricken arm. The twitching muscles made it look like worms wriggling under the skin.
Antivenin costs about $3,200 a vial. Why so expensive? First, lots of venomous snakes have to be captured. Their venom is extracted and injected into horses and sheep, whose blood forms antibodies against the poison. Finally, the animal blood is made into a product to treat humans.
Eventually Wasilewski improved. Opened his eyes. Talked. Then suffered a relapse. His blood had stopped clotting again. The swollen arm was turning black. Over the next three days his doctor ordered another 32 vials. Joe endured tubes up his nose, down his throat, in his penis, in his arm. Morphine. Fog. Day, night, another day. Improvement. Awake. Tubes came out. Ate some food. For the first time in more than a week, this man who was used to being around rattlesnakes, felt alive.
"I can't take another bite like that,'' Joe told friends who stopped by his home after Joe was released from the hospital. Joe has two Eastern diamondbacks. He has decided that he'll keep one of them for educational purposes. The other he'll give to a pal in Central Florida in the venom business. It is amazing that this South Florida longtime reptile wrangler has no hard feelings. “It was my own fault,” said Wasilewski. “I got careless. It’s not the snake’s fault.”
If a situation can happen to this expert, imagine what can happen out of the blue when hiking, hunting, stacking wood, or camping in rattlesnake habitat without the right protection. Don't take a chance! When in the desert or woods -- anywhere rattlesnakes are known to live -- protect yourself with snake gaiters or snake boots. This type of snake bite protection enables YOU to "deliver everything you have" when it comes to not getting bitten.
Monday, November 04 2013
The Burmese python, a native of India and other parts of Asia, has recently become an out-of-control menace in the Florida Everglades. No one knows exactly how these snakes got out of control. The guess is that they most likely developed from pets released into the wild, either intentionally or in the aftermath of Hurricane Andrew in 1992. These snakes eat native species like alligators and endangered egrets, and are a threat to humans and their pets. These snakes have no natural predators, so wildlife officials are racing to control the python population. The U.S. Department of Agriculture received a patent in August for a trap that resembles a long, thin cage with a net at one end for the live capture of large, heavy snakes.
The Gainesville field station for the National Wildlife Research Center, which falls under the USDA, is preparing to test the trap in a natural enclosure that contains five pythons. Over the coming months, the researchers will try baiting the traps with the scent of rats and python pheromones. The wire traps will be camouflaged as pipes or other small, covered spaces where pythons like to hide. The 5-foot-long trap is made from galvanized steel wire with a tightly woven net secured to one end. Two separate triggers need to be tripped simultaneously for it to close, which should keep it from snapping shut on such native snakes as the eastern diamondback rattlesnake or the water moccasin. Of course a pair of snake gaiters will keep humans from being bitten by rattlesnakes and other deadly vipers, but gaiters, boots or chaps won't protect you from pythons.
In an effort to control the snake population, the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission allows hunters with special permits to remove pythons and other exotic reptiles from some state lands. Earlier this year, a state-sanctioned hunt that attracted worldwide media attention was held. Roughly 1,600 amateur python hunters joined the permit holders for a month, netting a total of 68 snakes. A prolonged cold snap has proven to be one of the better methods of python population control, killing off large numbers of the snakes in 2010. The population rebounded, though, because low temperatures aren't reliable in subtropical South Florida. And with plentiful food around, the pythons can get really big! The longest python ever caught in Florida was an 18-foot-8-inch specimen found in May beside a rural Miami-Dade County road.
Everglades National Park encompasses 1.5 million acres, and all but roughly 100,000 acres of that is largely inaccessible swampland and sawgrass, so it's not easy tracking down Burmese pythons. The new traps are definitely an experiment. It may work, or it may not. Traps have been used in the park to collect pythons for research, but not for population control. The area may turn out to be too vast for steel traps to be effective. Time will tell.
|